Historical Background and Evolution
The Dutch Shepherd's legacy starts in the countryside landscapes of the Netherlands, where these flexible dogs served as indispensable assistants to agricultural workers. Their heritage dates back to the beginning of the 1800s, when they were developed to be versatile farm dogs able to tending flocks, drawing carts, protecting children, and protecting the farmstead.
During the period of industrialization and the subsequent reduction of sheep herding in the Netherlands, these dogs proved their flexibility by moving into various working roles. Their quantity declined dramatically during World War II, but dedicated breeders succeeded to preserve the breed.
Breed Characteristics
The Dutch Shepherd shows a moderately proportioned frame with well-developed physical development. The breed features three different coat varieties: smooth-coated, long-haired, and rough-coated. Each variety exhibits the distinctive brindle marking, which ranges from sandy to dark silver or graphite.
Their head displays a wedge-shaped form with moderate elliptical eyes that express awareness. The ears are carried erect and are moderately sized, contributing to their attentive countenance.
Temperament and Psychological Traits
Present-day Dutch Shepherds preserve the smart and diligent nature of their forebears. They exhibit remarkable analytical capabilities combined with a powerful motivation to work. These dogs develop powerful bonds with their owners while preserving a natural protective tendency.
Their intellect shows in their quick comprehension aptitudes and flexibility to various instruction techniques. They succeed in activities that test both their corporeal and cognitive faculties.
Exercise Requirements
Dutch Shepherds need significant routine exercise to maintain their physical and psychological health. Optimally, they should get a minimum of two hours of physical engagement each day, including various forms of activity.
Fitting pursuits involve long walks, trotting, aquatic exercise, obstacle courses, and play sessions. Intellectual challenge is similarly crucial, accomplished through learning exercises, problem-solving games, and planned exercises.
Instruction Methodology
Productive training of a Dutch Shepherd demands a measured approach that blends consistency with positive reinforcement. These dogs reply optimally to precise instruction and steady standards.
Beginning socialization is crucial, starting from young age. Puppies should be introduced to different persons, animals, environments, and situations to develop confidence and social competence.
Health Considerations
While usually healthy, Dutch Shepherds can be predisposed to certain health problems. Frequent concerns include hip abnormalities, elbow problems, PRA, and inflammatory myopathy.
Preventative measures involves regular veterinary check-ups, proper immunization schedules, and periodic oral hygiene. Keeping a healthy physical condition through appropriate nutrition and physical activity is essential.
Nutrition Recommendations
Suitable nutrition is vital for supporting the Dutch Shepherd's health and vigor. These energetic dogs require superior protein content and balanced nourishment to maintain their body structure and activity needs.
Portion sizes should be adapted based on the dog's age, exercise routine, and general condition. Puppies require precisely measured nutrition to ensure proper maturation.
Integration into Family Life
Dutch Shepherds can adjust wonderfully to family life when their requirements for exercise, instruction, and mental stimulation are fulfilled. They create powerful attachments with their family and can excel in homes with kids when properly socialized.
Their watchful nature makes them naturally watchful, yet they remain judicious and typically show proper judgment in their responses to possible threats.
Professional Duties and Modern Applications
Modern Dutch Shepherds thrive in diverse working positions that display their versatility. In police work, they execute crucial tasks including surveillance, substance identification, and suspect tracking. Defense organizations worldwide utilize their abilities in multiple missions, including detection work and surveillance tasks.
Emergency response groups value their tracking abilities and dedication in both outdoor and city locations. Their mental capacity and adaptability make them excellent service dogs for different support functions.
Sport Venues
In the realm of competitive activities, Dutch Shepherds display outstanding versatility. They excel in protection sports such as IPO, Ring Sport, and Dutch police dog trials. Their athletic ability extends to agility competitions, command competitions, and tracking events.
Success in competitive venues requires careful training. Physical conditioning encompasses appropriate warm-up routines, organized practice, and adequate rehabilitation time.
Advanced Genetics Aspects
Professional breeding of Dutch Shepherds requires a comprehensive grasp of genetics and characteristic features. Successful breeding plans evaluate not only structural features but also character, performance capability, and medical certifications.
Hereditary variation plays a crucial factor in protecting breed wellness and preventing inherited disorders. Developers must thoroughly assess mating candidates for genetic compatibility and physical wellness.
Senior Care and Aging Years
As Dutch Shepherds enter their mature years, their maintenance needs change. Senior dogs require modified physical programs, specific nutrition, and heightened medical care.
Movement should be modified to suit their changing capacities while preserving body strength. Mental stimulation stays crucial, accomplished through gentle training and stimulating pursuits.
Living get more info Conditions
Dutch Shepherds adjust to various living situations but thrive in environments that supply ample area for activity. A protected outdoor area supplies opportunities for spontaneous activity and entertainment.
Weather factors affect each coat form distinctly. Smooth-coated dogs may require supplementary covering in winter conditions, while heavy-coated varieties require extra care in hot conditions.
Social Behavior
The Dutch Shepherd's pastoral background shapes their interactive patterns and engagement with both individuals and other animals. They generally exhibit strong group sensitivity and demand clear guidance from their handlers.
Their herding instincts can manifest in different manners, from careful direction of household inhabitants to more intense pastoral activities with creatures or other pets.
Upcoming Progress
The outlook of the Dutch Shepherd lineage relies upon mindful breeding practices and preservation of their functional capabilities. Present-day development efforts focus on maintaining the breed's adaptability while guaranteeing hereditary wellness.
Continued evolution in professional duties and sports provides new opportunities for these adaptable dogs to show their abilities and add value to our communities.
 Anna Chlumsky Then & Now!
Anna Chlumsky Then & Now! Michael Bower Then & Now!
Michael Bower Then & Now! Jenna Von Oy Then & Now!
Jenna Von Oy Then & Now! Marla Sokoloff Then & Now!
Marla Sokoloff Then & Now!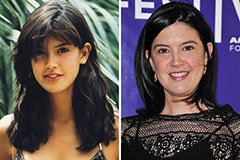 Phoebe Cates Then & Now!
Phoebe Cates Then & Now!